The article presents the data on onychomycosis causative agents, clinical types and forms of the nails affection, describes modern methods of onychomycosis treatment with the use of highly effective antifungal drugs of systemic and external action. It is shown that the cure of onychomycosis can be achieved by choosing the correct antimycotic preparations while taking into consideration the type and form of the lesion, the extension of the process, and the general state of the organism (related diseases, state of the immune system).
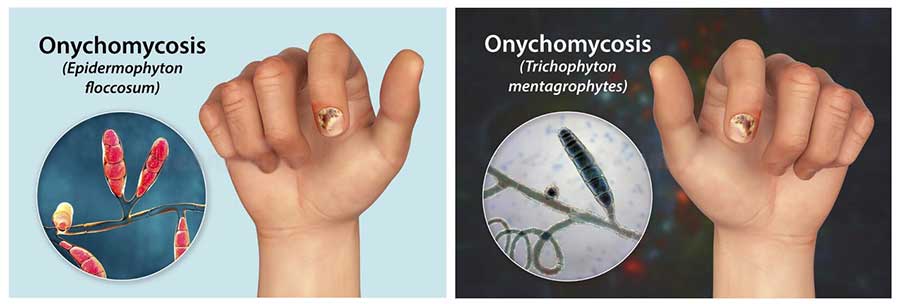
Over the past 20 years, mycosis of the feet (hands) has been the most common fungal disease worldwide, also affecting the nail plates in 40% of cases. The causative agents of onychomycosis can be dermatophytes, yeasts and molds. Of all the dermatophytes, the main causative agent is thought to be Trichophyton rubrum, which is isolated in 60-70% of cases by cultural examination. Fungus can affect the nail plates on the toes, hands, smooth skin on any area of the skin, as well as long and fuzzy hair.
The second pathogen, tryxorhton mentagrophytes var. interdigitale, affects only the nails on the I and V toes and the skin of the III-IV interfinger folds, the upper third of the sole, the lateral surfaces of the foot and toes and the arch of the foot. Very rarely, epidermophyton floccosum affects the nails on the I and V toes. Often, however, onychomycosis is caused by a mixed flora of Dermatophytes and yeast-like or mold fungi, and bacterial infection can also occur. From mould fungi, the most common pathogen is the fungus Scopulariopsis brevicaulis, The nails of the big toes are usually affected, the nails turn brown. Less commonly, mold onychomycosis can be caused by fungi of the genus Aspergillus, Alternaria, Acremonium, Fusarium and etc. Dermatophyte nail lesions can be distal when the nail begins to change from the free edge, lateral and proximal.
Several forms of nail lesions in onychomycosis: normotrophic, in which the nails retain a normal configuration, but become dull, with a yellowish tint at the free edge, with thickening in the corners of the nail plate due to accumulation of horny masses; hypertrophic – nail thickening over the entire surface due to subnail hyperkeratosis, nails become dull, dirty-gray color, loosened at the free edge; atrophic – the nails are considerably destroyed, they look like corroded from the free edge, the nail bed is partially exposed, covered with loose and dry crumbling masses; Onycholysis type of damage – the nail plates separate from the nail bed, become dull, sometimes of dirty-gray color; the nail remains of the normal color at the base. Combined nail lesions can occur in a single patient.
In recent years, significant advances have been made in the study of the causes of onychomycosis, particularly the possibility of spread Тrichorhophthon rubrum lymphohematogenous route. Trichophyton rubrum и Тrichorhton interdigitale can cause allergic rearrangement of the body, in addition, dermatophytes and some mold fungi can have a toxic effect on the body.
Onychomycosis treatment
Currently, mycologists have at their disposal a wide range of antifungal drugs of systemic and external action in various dosage forms (ointment, cream, solution, varnish, powder). However, the problem of treating patients with onychomycosis is still relevant, because the disease is often recurrent, it is difficult to treat candida onychiasis. Therapeutic efficacy, safety, route of administration, and cost should be the primary considerations when recommending a patient for a particular treatment. Antimycotics with fungicidal effect on various types of pathogens, the ability to accumulate in the nail matrix and nail bed are preferred for therapeutic effect. The method of treatment is important. When choosing a therapy, one should consider the type and form of the lesion, its distribution, duration of the disease, the speed of nail growth, and the patient’s general condition (related diseases, immune system condition, etc.д.).).
| There are currently 3 highly effective systemic antimycotics (terbinafine, itraconazole, fluconazole) and a number of topical therapies (bifonazole cream in a nail treatment kit, 5% amorolfin varnish, 8% cyclopyrox varnish, 1% bifonazole cream, 1% terbinafine cream, 1% cyclopyrox cream and solution, 1% naphthifine cream, 1% econazole cream, 1% isoconazole cream, 2% ketoconazole cream, 1% clotrimazole cream and solution, etc.). |
Treatment with antimycotics of systemic action
Treatment with systemic antimycotics is carried out without removing the nail plates. The daily dose of terbinafine for adults is 250 mg taken once a day or 125 mg twice a day with or after meals daily. The treatment duration is from 6 weeks to 3 months. Depending on the age of the patient, shape and area of the lesion. It is possible to shorten the duration of treatment by mechanical removal of the stratum corneum, especially in the hypertrophic form. Side effects such as nausea, discomfort or discomfort in the gastrointestinal tract may occur during the first days of treatment. Contraindications to the prescription of terbinafine are pregnancy and individual sensitivity to the drug.
In onychomycosis of feet (hands) caused by dermatophytes, mold, yeast-like fungi and mixed flora, itraconazole may be treated using the intermittent method: 200 mg (2 capsules) 2 times a day after meals for 7 days, followed by a 3-week break. For onychomycosis caused by dermatophytes or yeasts, cycles of 3-7 days are sufficient. 2-3 cycles in mold onychomycosis and 4 cycles in elderly patients with delayed nail growth.
In cases of onychomycosis of the hands, especially in young patients, therapeutic effect may be achieved after 2 cycles of therapy. Studies of the pharmacokinetics of itraconazole in nail tissues have shown that the drug penetrates the nail plate through the nail matrix as well as by diffusion from the nail bed, and persists in nail infection for 6 months. After 3 cycles of therapy, the duration of treatment depends on the area of the nail and the growth rate of the nail plate. Itraconazole is not recommended for use in onychomycosis in patients with liver or kidney dysfunction, pregnant and lactating women. Corrective therapy is prescribed in cases of decreased stomach acidity. Tolerability of itraconazole is good. Side effects are possible, but rare (gastrointestinal disorders, skin itching, fatigue, heaviness in the head), they pass without cancelling the drug.
Candida paronychiae and onychiae can be effectively treated with fluconazole. 200 mg daily after meals (first day, double dose 400 mg) daily for 3 to 4 months. Fluconazole treatment can be combined with external antifungal drugs: bifonazole, cyclopyrox, clotrimazole, isoconazole in the form of cream or solution. Bifonazole is rubbed into the roller area once in the evening, the other drugs twice a day.
Topical therapy
If there are contraindications to the use of systemic antimycotics, patients with onychomycosis of the feet (hands) may be prescribed bifonazole cream in a nail treatment kit in combination with 1% bifonazole cream, 5% amorolfin varnish, 8% cyclopyrox varnish. Treatment with bifonazole cream in a nail treatment kit consists of two steps. In the first stage, a cream consisting of bifonazole and urea is applied to the affected nails. The cream is applied to the affected area of the nail under the occlusion bandage using a dispenser, spread over the nail surface and left for 24 hours. Under a waterproof plaster. Before each application of the cream, change the dressing, prepare a warm bath and remove the easily separated part of the affected nail with a special file. The use of the cream continues until the nail plate or part of it is removed. Our results show that the nail plate can be painlessly removed in layers over a period of 4 to 28 days (16 days on average) with this formulation, the nail bed is treated at the same time. The patient should be warned that nail removal should only be performed according to the specified technique and no blade should be used. Subsequent therapy consists of treating the bed with 1% cream with bifonazole for 4 weeks or longer, depending on the degree of nail damage. The cream is rubbed into the nail bed once a day, at the same time it is applied to the foot skin and interfinger folds in the evening after washing and drying the feet. Clinical observation and mycological studies before treatment, after nail detachment, at the end of treatment, then after 1, 3, 6, 12 months. After the end of treatment. The growth of healthy nails is observed within 1, 5 to 4 months in distal type, 6 to 12 months in distal-proximal type, but not all patients get cured, in proximal type clinical improvement is observed. Note the good tolerance of bifonazole cream for nail treatment, which allows this method to be used in patients with onychomycosis and foot eczema.
Treatment of eczema may be given at the same time. Nail cream with bifonazole may be widely used in older patients. For onychomycosis caused by dermatophytes, yeasts and molds, up to 80% of the lesion, with an intact nail bed and nail bed, 5% varnish and 0.25% amorolfin cream. Nail polish should be applied to the affected finger or hand nails once every 7 days. Affected nails must be removed with the nail file that comes with the nail polish before use. Then the nail surface should be cleaned and degreased with an alcohol swab. If nail polish is reapplied, infected nail areas should be removed again with a nail file. Remove nail polish residue with an alcohol swab before treatment. On the skin of the feet, palms and hands apply 0.25% amorolfin cream once a day in the evening. The treatment is continued until healthy nails have grown back. The course of treatment depends on the stage and form of the lesion, location of the mycosis and is equal to 6 months in case of onychomycosis of the hands and 9-12 months – in case of legs.
Treatment on the skin until clinical signs have resolved (at least 2-6 weeks) and for several days after clinical recovery. Tolerability of varnish and cream is satisfactory, sometimes there may be a slight transient burning sensation of the nails, and when using the cream – a slight skin irritation (hyperemia, itching, burning sensation). The nail polish is contraindicated in case of hypersensitivity.
If the distal onychomycosis is caused by dermatophytes, yeasts and molds, you can use 8% cyclopyrox varnish Combined with 1% cream or 1% cyclopyrox solution. Before applying the nail polish, most of the affected nail is removed with a nail file and trimmed to create an uneven surface. Apply nail polish in a thin layer once a day. Once a week, remove the nail polish layer with a nail polish remover. Treatment continued for 1 month. Then nail polish is applied twice a week for one month and once a week after the third month. The duration of treatment depends on the form of the lesion, but should not exceed 6 months. Cyclopyrox cream or solution is applied to the skin twice a day (at least for 2 weeks).). Once clinical manifestations have resolved, use the product for another 1-2 weeks to prevent a relapse. In case of distal onychomycosis the infected part of the nail may be cleaned with bifonazole nail treatment cream, and then the nail bed may be rubbed twice a day or a broad-spectrum antimycotic for external use (exoderil, econazole, ketoconazole, terbinafine, bifonazole, clotrimazole, etc.) may be applied under the dressing.). Simultaneous treatment of smooth skin on the feet or hands until clinical manifestations resolve. The duration of the treatment is from 6 to 12 months and more, until the nails grow out. Based on the long-term experience, we believe that the therapeutic effect in the treatment of onychomycosis depends on the correct choice of an antifungal agent, taking into account the type, type of nail damage and the spread of the process, as well as on the regular disinfection of shoes (gloves) until the growth of healthy nails.

